Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Managing diabetes requires constant monitoring, medication, and lifestyle changes. But did you know that data plays a crucial role in effective diabetic care?
Yes, you read that right! Data holds the key to managing diabetes better and ensuring continuity of care. In this blog post, we will explore why storing health data is essential for effective treatment and how electronic health records (EHR) can make a significant difference in diabetic care. So sit back, relax and get ready to discover the link between diabetes and data!
Meet Dr.Sivakumar
Dr. Sivakumar is a diabetic care practitioner based in a tier 2 city in India. His journey began in 2004 when he started capturing digital health records on behalf of his patients at his clinic. This approach significantly reduced the burden on patients who no longer needed to carry physical paper records. Moreover, it enabled Dr. Sivakumar to provide better care by facilitating easy retrieval of vital parameters such as blood sugar levels, pulse, BMI, and blood pressure. Additionally, the digitization of health records allowed him to provide printed prescriptions, which increased patient compliance compared to the traditional method of handwritten prescriptions.
In 2009, Dr. Sivakumar and his team built an electronic medical records (EMR) system for their clinic with the help of a software development company. This implementation resulted in a reduction in operational tasks, freeing up more time for providing enhanced care to patients. By using the EMR system, Dr. Sivakumar was able to identify prescription patterns and deliver faster and more effective medications to his patients. The system also provided the ability to visualize trends in vital parameters and review past performance, enabling him to make prompt and informed decisions in patient care.
About our App
Recognizing the importance of continuity of care, Dr. Sivakumar and his team introduced a progressive web app in 2019. This mobile app allowed patients to hold their health records digitally and empowered them to take control of their healthcare. Through the app, patients could conveniently schedule online appointments, engage in doctor-patient chats, and record their vitals at home. This comprehensive approach fostered better adherence to treatment plans, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes
Dr. Sivakumar's journey exemplifies the positive impact of incorporating digital health solutions into medical practice. By embracing technology and continually seeking innovative ways to leverage it, he has not only enhanced the efficiency of his clinic but also empowered his patients to actively participate in their own care. His dedication to providing excellent healthcare and his forward-thinking approach set an example for the medical community at large.
The link between diabetes and data
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide, and managing it requires continuous monitoring and treatment. This is where health data comes in, as it plays a crucial role in tracking the progress of diabetic care. Data can be collected through various means such as blood sugar tests, medication logs, exercise routines, and diet plans. All this information helps healthcare providers understand how diabetes is affecting the body and allows them to adjust treatments accordingly.
Moreover, data enables healthcare professionals to identify potential complications before they become severe. For instance, if high blood sugar levels are detected early on through regular testing and recording data with an EHR system or electronic health record software , doctors can take preventive measures to avoid serious consequences such as heart attacks or strokes.
Case Study 1
Patient- 143593,63-year-old female who was diagnosed to have Type 2 Diabetes due to severe hyperglycemia in August 2019. She presented with severe polyuria and found to have fasting sugar 275 mg/dl and Postprandial sugar of 383 mg/dl and HbA1c of 15%.
Guidelines recommend initial insulin due to severe symptoms. But she declined to have insulin. So she was prescribed to have Metformin with Voglibose once daily in the morning. Pioglitazone 15mg with Metformin 500mg as a combo at night half tablet. Vildagliptin 50 mg once daily in the morning. A stat dose of 16 units of insulin Glargine was given.
Tabulation
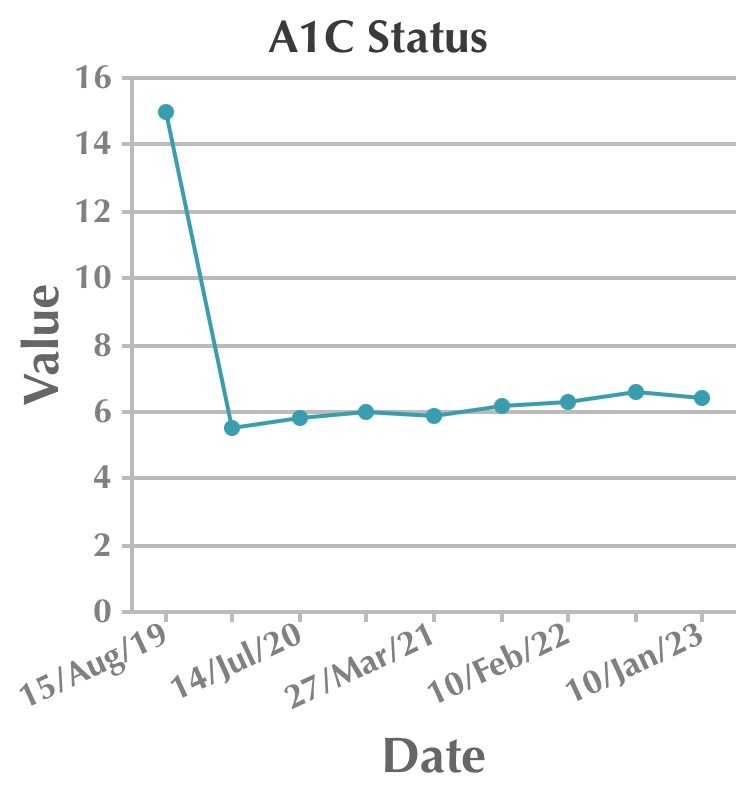
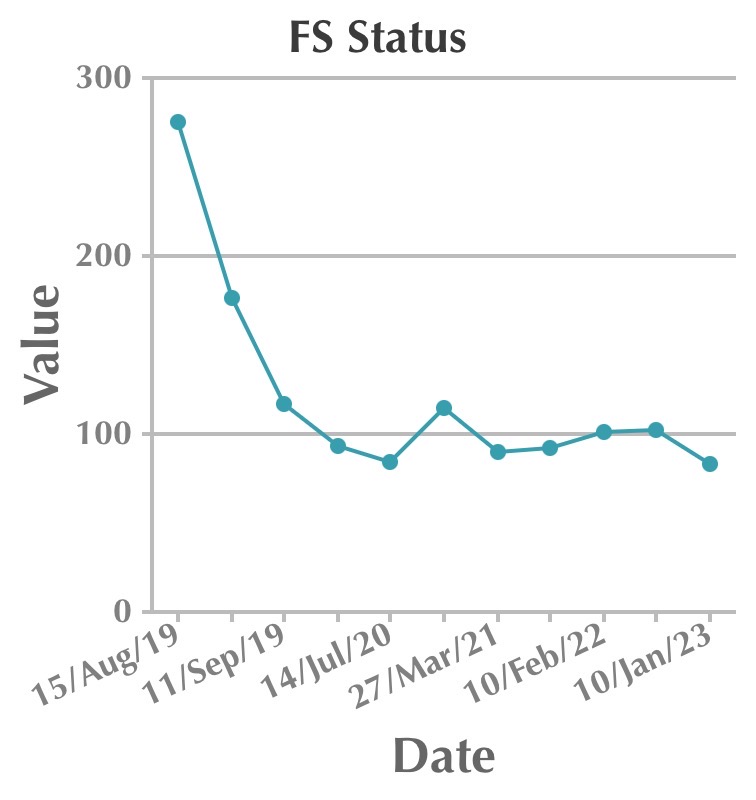
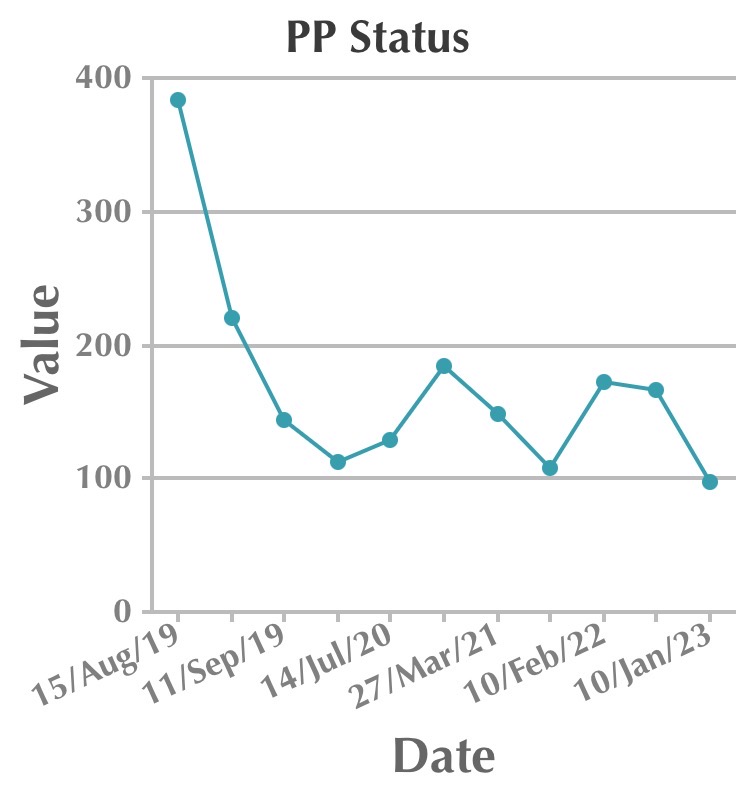
Follow up visits and medications tabulated. We can observe de-escalation of drugs and doses over a period when there is good follow-up and proper adherence to the therapy.
| Date | Fasting | Postprandial | HbA1c | Metformin | Pioglitazone | Vildagliptin | Voglibose | Gliflozin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15th August 2019 | 275 | 383 | 15 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| 23rd August 2019 | 176 | 220 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| 11th September 2019 | 117 | 144 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| 14th November 2019 | 93 | 112 | 5.505 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| 14th July 2020 | 84 | 129 | 5.8 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| 17th November 2020 | 115 | 184 | 6.0 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| 17th November 2020 | 115 | 184 | 6.0 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| 27th March 2021 | 90 | 148 | 5.9 | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | |
| 20th August 2021 | 92 | 108 | 6.2 | Yes | No | Yes | No | |
| 10th February 2022 | 101 | 173 | 6.3 | No | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| 23rd July 2022 | 102 | 166 | 6.6 | No | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| 10th January 2023 | 83 | 98 | 6.4 | No | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Row Data | Row Data | Row Data | Row Data | Row Data | Row Data | Row Data | Row Data | Row Data |
Chart
Follow up visits and medications tabulated. We can observe de-escalation of drugs and doses over a period when there is good follow-up and proper adherence to the therapy.

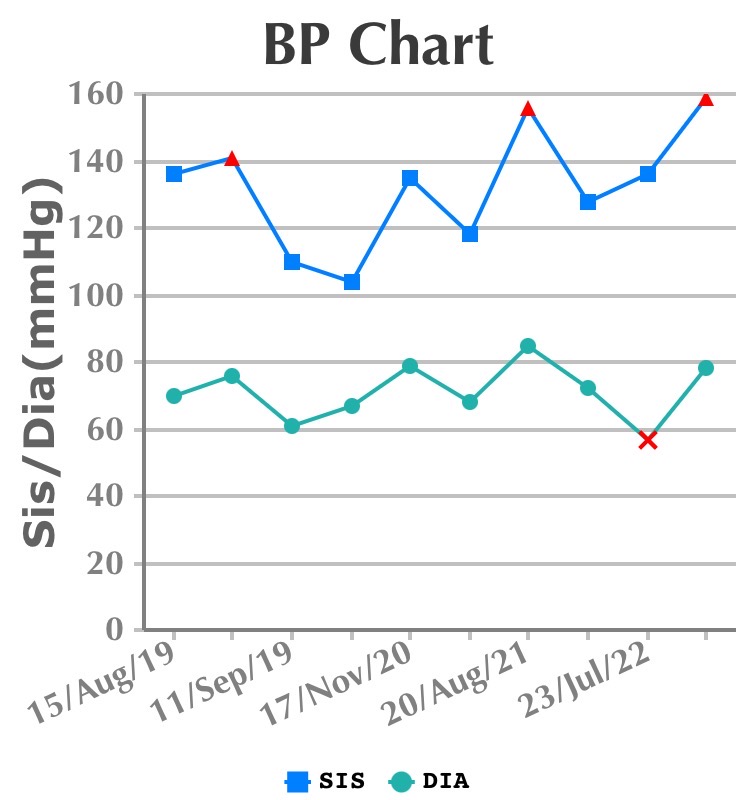
Result
It is possible with the help of current armamentarium of treatment to control hyperglycaemia in effective way on a long-term basis. What the patient was following is simple less calorie diet adaptable easily in daily basis, no intense physical exercises but proper medication.
It is not that, we should not advise life style modification. But right combination of adaptable diet, exercise and drugs might work wonder with affordable medications currently available. Beautiful part is never started with SU.
Case Study 2
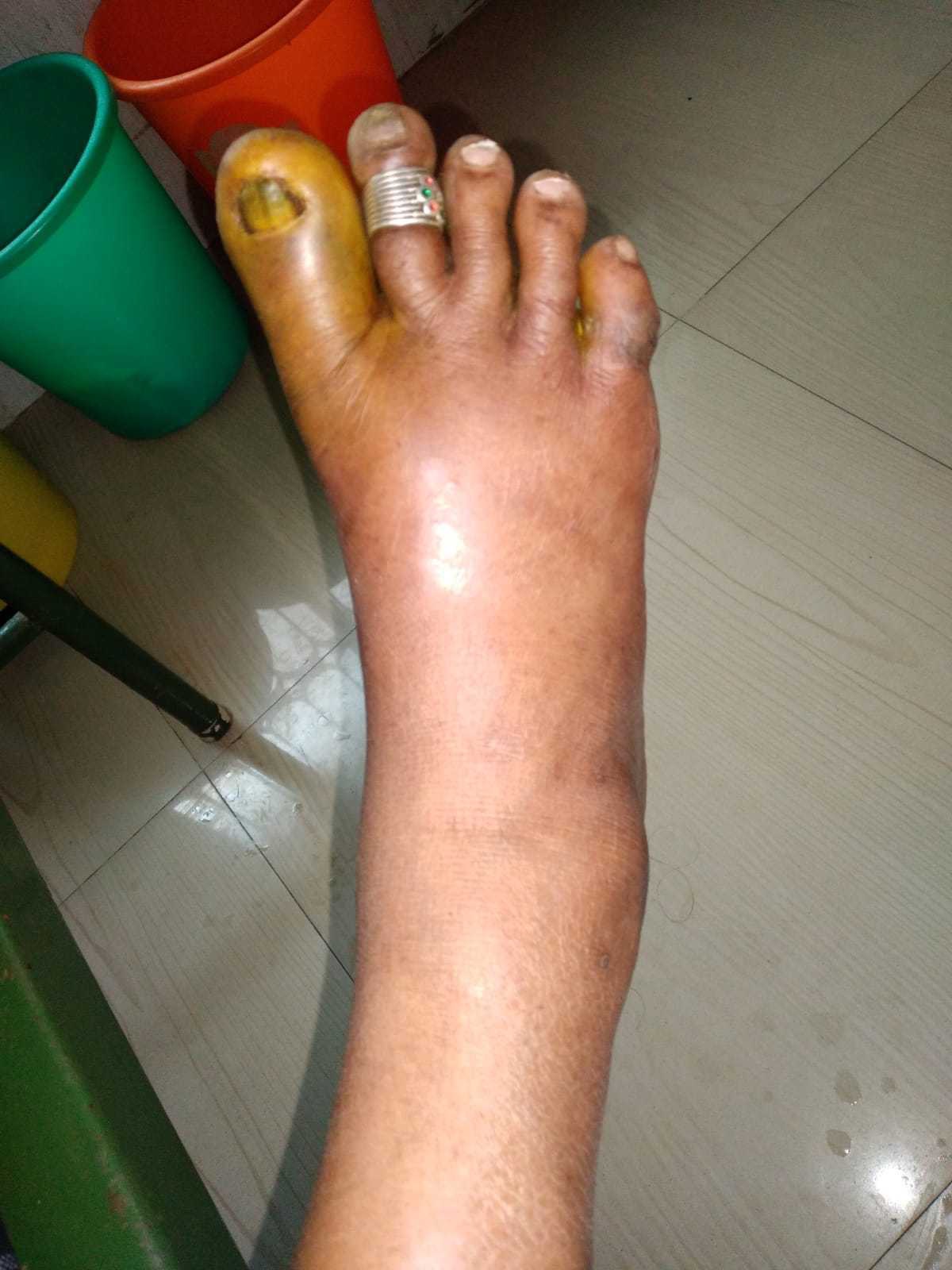
Patient-151771 year female who visited the hospital for the first time in November 2022 who is known person of type2 diabetes since 2020 (2 years duration), presenting with high sugar values with a history of poor appetite as main symptoms. In the past she never considered control of diabetes as important.
As glucose values were very high, she was initiated to have basal insulin at bedtime with oral anti diabetic agents in the morning.She failed to have irregular follow up and on January 2023 she landed here again with poor diabetes control because she did not continue insulin and Other medications properly for the past month. On clinical examination she was found to have severe cellulitis right footand got admitted for control of diabetes as well As control of foot infection.
Tabulation
Follow up visits and medications tabulated. We can observe de-escalation of drugs and doses over a period when there is good follow-up and proper adherence to the therapy.
| Date | Fasting | Postprandial | HbA1c | Metformin | Voglibose | Insulin - Glargine | Gliptin | SU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11th November 2022 | 290 | 489 | 13.2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | - | - |
| 1st December 2022 | 184 | 468 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | - |
| 19th January 2023 | 205 | 460 | admitted and started with basal bolus insulin along with antibiotics | - | - | Yes | - | - |
Why data is important in diabetic care
Data plays a crucial role in diabetic care. With the increasing prevalence of diabetes worldwide, managing this chronic disease can be challenging for healthcare providers. This is where data comes into play as it helps in providing effective treatment and continuity of care.
By collecting and analyzing health data, healthcare professionals can gain insights into patients' glucose levels, medication adherence, lifestyle habits and other important metrics that are critical to manage diabetes effectively. The use of Electronic Health Records (EHR) has made it easier for clinicians to collect patient data efficiently and securely. The ability to access patient information from multiple sources allows doctors to make informed decisions about diabetic care. They can track changes in blood sugar levels over time, monitor the effectiveness of medications or lifestyle interventions prescribed by them, and provide personalised recommendations based on individual needs.
Moreover, sharing health information across different healthcare settings enhances continuity of care which means improved outcomes for patients with diabetes. It enables better communication between primary physicians, specialists or even emergency responders at times when immediate intervention may be necessary due to complications arising from diabetes.
Storing data related to patient's diabetic management is essential as it provides valuable insights that help improve the quality of care provided by healthcare professionals. By leveraging EHRs and otherdigital tools available today we can achieve better outcomes for individuals living with diabetes while promoting overall population health.
Conclusion
Storing health data is crucial for providing effective treatment and ensuring continuity of care for diabetic patients. With the help of electronic health records (EHRs) and other technological advancements, healthcare providers can easily access patient information and make informed decisions about their care.
By utilizing data analytics tools, medical professionals can identify patterns in a patient's blood sugar levels and other vital signs to create personalized treatment plans. This not only improves outcomes but also enhances the patient experience by reducing hospital readmissions and unnecessary appointments.
Furthermore, storing health data allows researchers to gain insights into diabetes management that may lead to new treatments or even a cure someday. Thus essential that we continue to prioritise the collection and storage of accurate and comprehensive health data for diabetic patients.
